Imagine this: You’re Ravi Patel, running a thriving textile factory in Surat. Your fabrics are known for their quality, but a new competitor has emerged, offering lower prices and faster turnaround times.
You know you need to make changes, but where do you even begin?
This is a familiar story for countless small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in India. MSMEs are the backbone of the Indian economy, contributing over 30% of India’s GDP. However, they also face fierce competition, not just from established players but also from new, agile entrants.
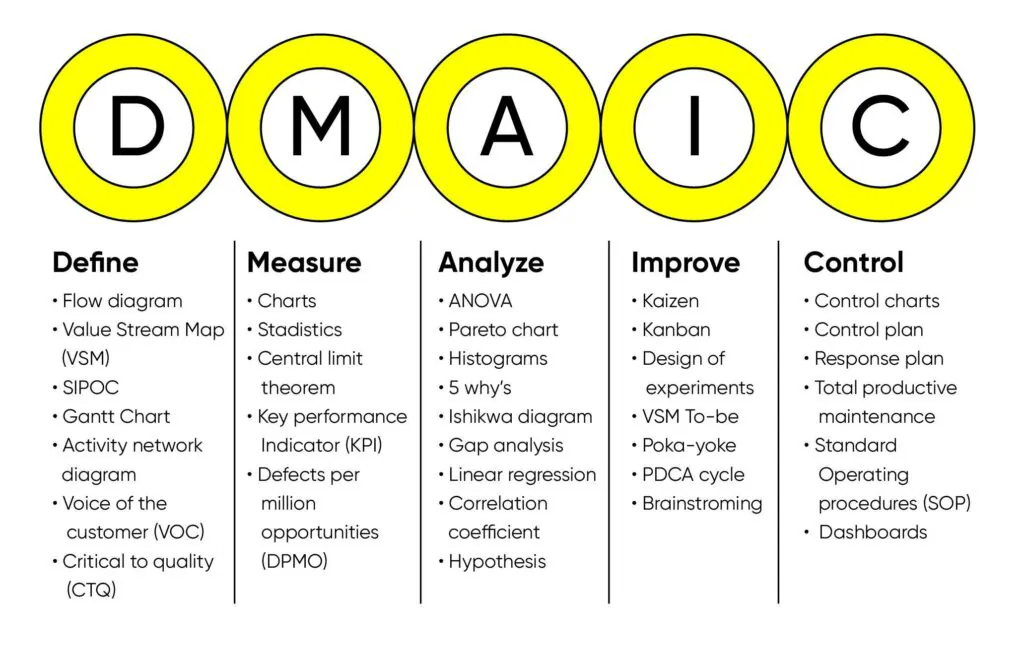
Here’s where DMAIC, a powerful problem-solving methodology, comes in. DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It’s a structured approach that can help businesses like yours identify areas for improvement, implement changes, and achieve sustainable success.
Breaking Down the DMAIC Process:
DMAIC is a cyclical process, meaning you can revisit and refine each step as needed. Let’s delve into each stage:
- Define: Clearly identify the problem you’re trying to solve. For Ravi, it’s the decline in sales due to competitor pricing and speed.
- Measure: Gather data to understand the problem’s scope. Ravi might calculate that sales have dropped by 20% in the last quarter, with a 30% decrease in bulk orders from major garment manufacturers. He can also measure his competitor’s turnaround time compared to his own.
- Analyze: This is where detective work comes in. Ravi observes his factory processes. He might notice inefficiencies in fabric cutting, delays in dyeing due to ageing equipment, and a lack of automation in some areas.
- Improve: Based on his analysis, Ravi devises a plan. He could explore options for bulk fabric discounts with suppliers, invest in newer, faster dyeing machinery, and consider partial automation in the cutting section.
- Control: After implementing changes, Ravi monitors progress. He tracks production times, customer satisfaction, and production costs. He also establishes control measures to prevent regression, such as preventive maintenance schedules for new equipment and standardized operating procedures for fabric cutting.
The Benefits of DMAIC for SMEs:
- Structured approach: DMAIC provides a clear roadmap for tackling problems, preventing you from getting lost in the weeds.
- Data-driven decision-making: Emotions are great for designing beautiful fabrics, but running a business requires data-driven decisions. DMAIC encourages you to base your choices on facts and figures.
- Focus on customer requirements: Faster turnaround times at competitive prices – that’s what Ravi’s customers need. DMAIC helps you identify and address those needs.
- Identification of root causes: Going beyond surface-level issues, DMAIC helps you unearth the root cause of problems, leading to more effective solutions. In Ravi’s case, it wasn’t just competitor pricing; it was inefficiencies within his own factory.
- Continuous improvement culture: DMAIC isn’t a one-time fix; it’s a philosophy that encourages you to constantly seek ways to improve your processes and stay ahead of the curve.
Real-world Examples of DMAIC in Action:
- The tale of Ashok, a chemical manufacturer in Chennai: Facing rising production costs and environmental concerns, Ashok used DMAIC to optimize his chemical processes. By identifying inefficiencies in raw material usage and implementing green technologies, he reduced costs and minimized environmental impact.
- Revamping the supply chain for Bengaluru-based Green Tech Company: With a growing order book, this green energy solutions provider used DMAIC to streamline its supply chain. By identifying bottlenecks in component procurement and partnering with local vendors, they achieved faster delivery times and improved customer satisfaction.
Beyond Manufacturing: DMAIC for Every Business!
The beauty of DMAIC is its versatility. Here are some examples from other sectors:
- A travel agency in Delhi: Use DMAIC to identify customer pain points and personalize travel packages for better satisfaction.
- A healthcare facility in Mumbai: Implement DMAIC to reduce waiting times for patients and improve overall patient experience.
Getting Started with DMAIC:
DMAIC may seem complex, but it’s a surprisingly user-friendly framework. Here are some resources to help you get started:
- The American Society for Quality (ASQ) offers a wealth of DMAIC resources, including training courses and certification programs.
- Several online platforms offer free DMAIC templates and tutorials.
- Consultants like Stratefix Consulting, specializing in DMAIC can provide guidance and support for your specific business needs.
In today’s competitive landscape, India’s SMEs need a powerful tool to thrive. DMAIC provides a structured, data-driven approach to problem-solving and continuous improvement.
FAQs and Beyond DMAIC: A Gateway to Operational Excellence!
- Is DMAIC only used in manufacturing? No, DMAIC is applicable across all industries, from textiles and chemicals to healthcare and travel agencies.
- How long does a DMAIC project typically take? The duration can vary depending on the complexity of the problem. Simple projects might take weeks, while larger-scale initiatives could span months.
- What are some common tools used in DMAIC? Many tools can be used within DMAIC, such as process flow mapping, cause-and-effect diagrams, and Pareto charts. We’ll delve deeper into these tools in future posts.
- How does DMAIC differ from DMADV? DMAIC focuses on improving existing processes, while DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify) is used to create new products or services. We’ll explore DMADV in a future blog.
- Can DMAIC be combined with other improvement methodologies? Absolutely! DMAIC can be a powerful framework for integrating tools and concepts from Lean manufacturing, Six Sigma, and other methodologies. We’ll unpack these synergies in upcoming posts.
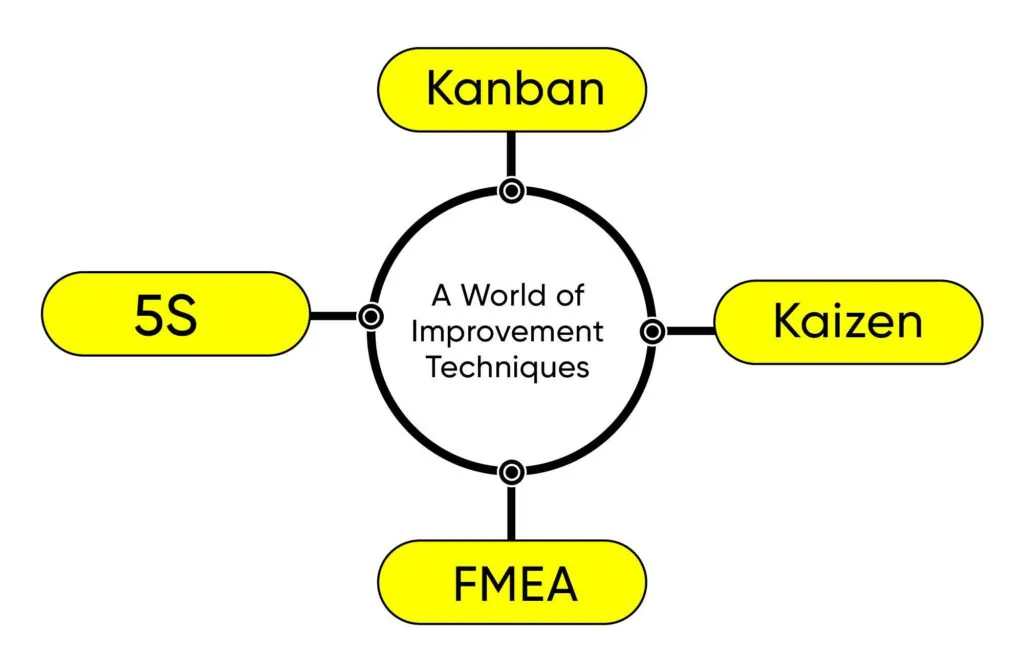
Beyond DMAIC: A World of Improvement Techniques
While DMAIC provides a solid foundation, there’s a whole arsenal of Lean Six Sigma methods and tools waiting to be explored in our upcoming blogs:
- 5S (Sort, Straighten, Shine, Standardize, Sustain): A foundational method for organizing workplaces for efficiency and safety. (Workplace organization for efficiency)
- Kanban: A visual system for managing work in progress, ensuring smooth workflow. (Visual tool for workflow management)
- Kaizen: The philosophy of continuous improvement, small but steady steps towards better. (Continuous improvement philosophy)
- FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis): Proactively identifying potential failures and their impact. (Identifying potential failures proactively)
This blog is Part 2 of our Lean Six Sigma series. Read the First Part Here about First Time Right (FTR), or Right First Time, is a concept from Total Quality Management (TQM) that is intended to ensure that activities are performed correctly the first time so that no rework is necessary. DMAIC is a cornerstone of Lean Six Sigma, which provides a structured approach to implementing and sustaining FTR!
Stay tuned for our upcoming blogs where we’ll delve deeper into these powerful tools and how they can help SME’s & MSMEs achieve operational excellence!







